Executive Summary
A study conducted in 2023 found that email-based attacks still account for nearly 20% of ransomware incidents in the education sector, impacting both higher and lower education. The increases in 2023 were significant:
-
80% increase in lower education, up 56% over 2022
-
79% increase in higher education, up 64% over 2022
-
30% of cyberattacks advanced phishing techniques
To combat these attacks, organizations should replicate real-world spear-phishing scenarios by using AI-driven simulations and training. This will help prepare employees to recognize and respond to advanced cyber threats, strengthening cybersecurity defenses against the human element. In this report, we have compiled a summary of the leading threats to the education sector and the tools that can mitigate these threats.
Understanding the primary means of attack, including compromised credentials, exploited vulnerabilities, and email-borne threats, is crucial to securing sensitive data and learning processes. Recognizing the differences in susceptibility between lower and higher education is also essential.
Key Areas of Vulnerability
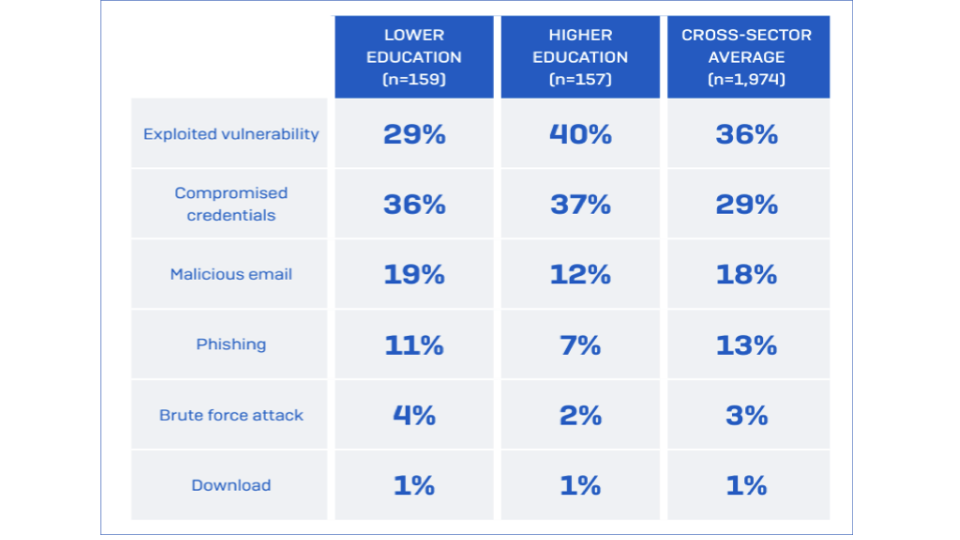
Lower Education
-
Compromised Credentials: 36% saw stealing login information as the primary gateway for an attack. This indicates potential weaknesses in password hygiene, limited use of multi-factor authentication (MFA), and a need for increased security awareness.
-
Email-Based Attacks: 30% of attacks originate from phishing or malicious links, demanding stringent email security measures and comprehensive user training.
Higher Education
- Exploited Vulnerabilities: 40% of ransomware attacks penetrated through unpatched or outdated software and systems. Prioritizing system updates and robust patching protocols is paramount.
-
Compromised Credentials: 37% of exploited vulnerabilities resulted from stolen credentials, which presents a significant threat. Strong password practices and MFA are non-negotiable.
-
Email-Based Attacks: These threats account for 19% of incidents, suggesting ongoing vigilance to email security is crucial.
Recommendations
-
Jericho Security's AI-Driven Simulation and Training: To address these challenges, Jericho Security’s platform offers AI-driven simulation and training. Replicating real-world spear-phishing scenarios prepares employees to recognize and respond to advanced cyber threats, thus reinforcing the human element of cybersecurity defenses.
Conclusion
Phishing remains the most dangerous threat to educational institutions. Understanding sector-specific vulnerabilities, implementing layered security measures, and ensuring constant awareness through training will significantly increase institutional resilience to these attacks.
1 https://www.sophos.com/en-us/whitepaper/state-of-ransomware-in-education
Figure 1: Root Causes of Ransomware Attacks in Education